Access Control
Access to each collection and resource within the Nuvla service is protected by an Access Control List (ACL). An ACL identifies the owners of the resources and “principals” with specific access rights. The both owners and principals take the form of a resource identifier within an ACL, for example, “group/nuvla-admin” or “user/0d20f265-af45-48a8-a32f-a8debd8c4e61”.
When user’s authenticate with Nuvla, their session contains a list of associated principals; this list is sometimes referred to as the user’s “claims”. The server evaluates an ACL using these claims to decide whether to grant access or not.
The ACL implementation provides fine-grained access control while, at the same time, allowing fast, database-level of the ACLs. One side-effect of the focus on database-level performance is that the support ACL syntax only allows for positive rights to be expressed. Rules like “user X is denied access to resource Y” cannot be expressed with the Nuvla ACLs.
Resource ACLs
Each resource contains an ACL that is stored along with the other attributes of the resource. Consequently, the ACL is expressed as a JSON object. An example of an ACL is:
{
"owners": ["group/nuvla-admin"],
"view-meta": ["group/nuvla-user", "user/37997228-baac-4744-b080-454ea7524258"],
"view-data": ["group/nuvla-user", "user/37997228-baac-4744-b080-454ea7524258"],
"view-acl": ["user/37997228-baac-4744-b080-454ea7524258"],
"edit-meta": ["user/37997228-baac-4744-b080-454ea7524258"],
"edit-data": ["user/37997228-baac-4744-b080-454ea7524258"],
"edit-acl": ["user/37997228-baac-4744-b080-454ea7524258"],
"delete": ["user/37997228-baac-4744-b080-454ea7524258"],
"manage": ["user/37997228-baac-4744-b080-454ea7524258"]
}
The owners always have full access to the resource; consequently, they do not need to be specified in the detailed rights that follow.
The view-meta/data/acl” rights allow the given principals to retrieve the associated segment of the resource. See below for a description of the three segments of a resource.
The edit-meta/data/acl” rights allow the given principals to modify the associated segment of the resource.
The delete and manage rights allow the given principals to delete or to run actions (“manage”) a resource, respectively. These actions include, for example, the “start” and “stop” actions of a deployment.
The above example shows a fully normalised ACL. The owner principals do not appear in the detailed rights lists and the rights for other principals are explicitly given, even though some rights imply others (see the hierarchy section below). ACLs are always normalized before they are stored. Clients may provide abbreviated ACLs, which will then be normalized by the server.
Resource Segments
Each resource contains three segments: meta, data, and acl. The view and edit rights for each of these segments is handled separately. The following diagram shows these segments.

The meta segment contains the metadata of the resource. It consists exclusively of the attributes: id, resource-type, subtype, created, updated, parent, and tags.
The acl segment consists of only the acl attribute.
The data segment consists of all attributes that are not in the meta and acl segments, excluding the operations attribute.
The other section consists of ephemeral attributes added dynamically by the server. These are not subject to access control. Currently, the operations attribute is the only ephemeral attribute.
Rights Hierarchy
As mentioned earlier, some rights imply other rights. The following diagram shows the full hierarchy of rights.
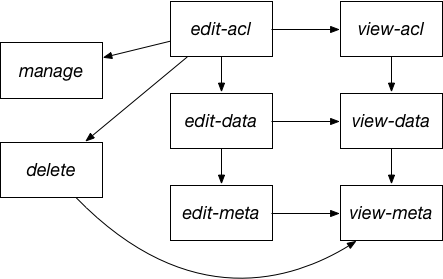
The edit-acl right implies all others and acts as an all rights identifier. This hierarchy is used when normalising an ACL to make all the rights explicit.
Collection ACLs
Access to resource collections are also governed by ACLs. However, these are set by the developer and cannot be modified by users of a Nuvla server.
The following shows an example of the ACL for the session resource collection:
{
"query": ["group/nuvla-anon"],
"add": ["group/nuvla-anon"]
}
There are only two rights: query and add. The add right governs who can add new resources to the collection. The query right governs who can search the collection.
NOTE: The content of any search respects the ACLs of the individual resources.
As these ACLs are specified by the developer, it only makes sense to include the special groups in these ACLs.
Special Groups
There are three special groups that can appear in ACLs:
- group/nuvla-admin: consists of all users who have administrator rights to the service. Administrators have all rights to all resources.
- group/nuvla-user: consists of all authenticated users on the platform. That is, any user who is logged in will have this group in their session claims.
- group/nuvla-anon: consists of all users of the platform, whether authenticated or not. All sessions will have this group in their claims.
The membership of the group/nuvla-admin can be managed by the administrators of the platform. Adding people to that group makes them administrators.
The other two groups are treated specially by the Nuvla server and do not have a list of users that can be maintained by the group resource.
